These are concepts in Javascript that developers tend to have a hard time understanding. In this article, I will simplify these concepts.
Map, Filter, and Reduce Methods.
These are all array methods in Javascript.
Each iterates over an array and performs the transformation/computation.
Each returns a new array based on the result of the function.
They don’t modify the original array.
They don’t execute for empty elements.
Always indicate a return statement in your callback. You will get a new undefined or empty array if you omit it.
They are all ‘higher order’ functions because they take user-defined functions as parameters.
Array.prototype.map()
It creates a new array from an existing one by calling a function for every array element.
It calls a function once for each array element.
In the callback function, return the data you wish to be part of the new array.
map() syntax
The syntax of the map() method is:
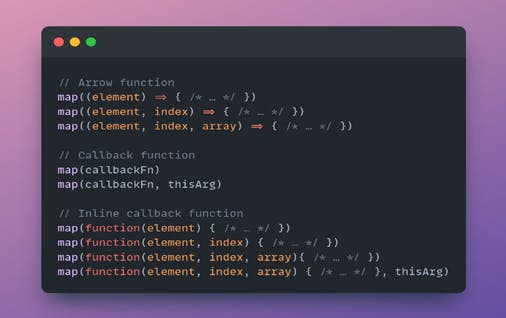
map() parameters
· callbackFn
Function that is called for every element of arr. Each time callbackFn executes, the returned value is added to newArray.
The function is called with the following arguments:
· element
The current element being processed in the array.
· index
The index of the current element being processed in the array.
· array
The array map was called upon.
· thisArg (Optional)
Value to use as this when executing callbackFn.
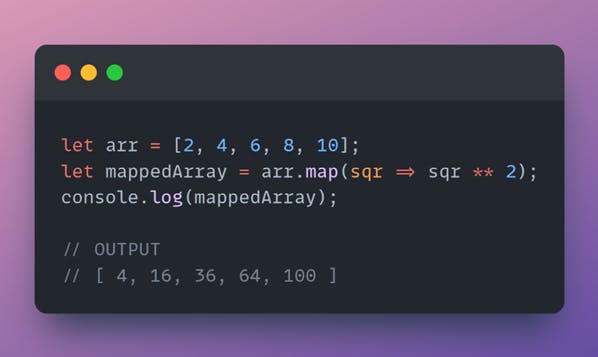
Map() example
Find the squared values of the array values.
Array.prototype.filter()
It returns a subset of the original array based on custom criteria.
In your callback, return a Boolean value to determine whether or not each item will be included in the new array.
filter() syntax
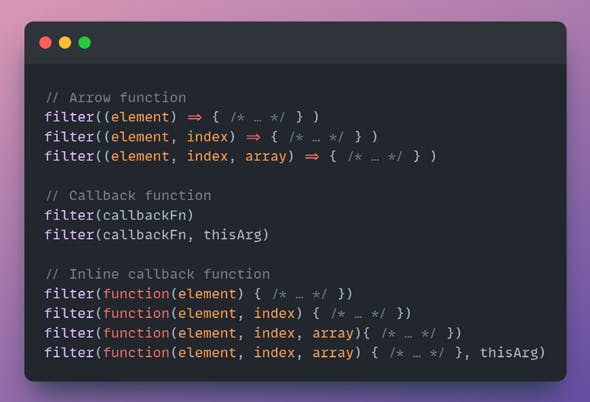
filter() parameters
·callbackFn
Function is a predicate, to test each element of the array. Return a value that coerces to true to keep the element, or to true otherwise.
The function is called with the following arguments:
·element
The current element being processed in the array.
·index
The index of the current element being processed in the array
·array
The array on which the filter() was called
·thisArg (optional)
Value to use as this when executing callbackFn
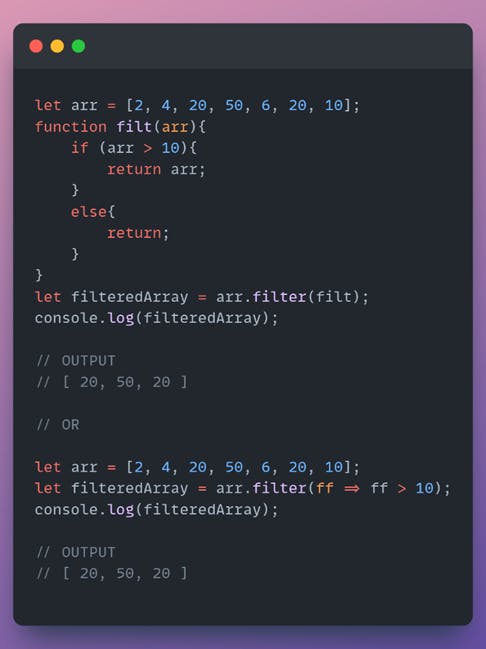
filter() example
Find all the numbers greater than 10.
Array.prototype.reduce()
This method reduces any array of values down to just one value.
To get the output value, it returns a reducer function on each array element.
It is often used to return a single number, but it can also be used to combine the logic of Map and Filter to return an array of values matching certain criteria.
The callback for Reduce has two parameters: the accumulator and the current value. Always return the accumulator after modification.
In addition to the callback, Reduce receives a second parameter that will define the initial value of the accumulator
reduce() syntax
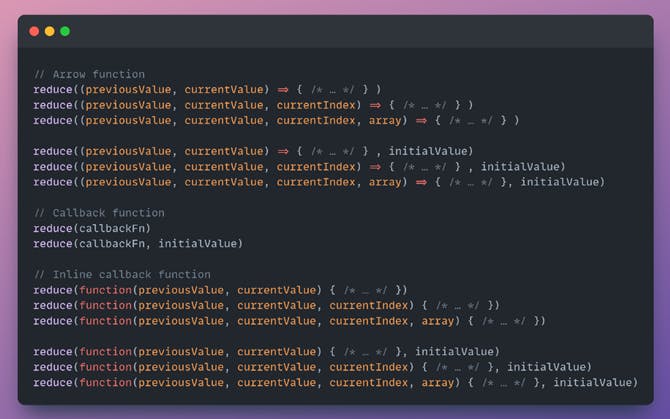
·callbackFn
A “reducer” function called with the following arguments:
·previousValue
The value resulting from the previous call to callbackFn. On first call, initialValue if specified, otherwise the value of array[0].
·currentValue
The value of the current element. On first call, the value of array[0] if an initialValue was specified, otherwise the value of array[1].
·currentIndex
The index position of currentValue in the array. On first call, 0 if initialValue was specified, otherwise 1
·array
The array being traversed.
·initialValue (optional)
A value to which previousValue is initialized the first time the callback is called. If initialValue is specified, that also causes currentValue to be initialized to the first value in the array. If initialValue is not specified, previousValue is initialized to the first value in the array, and currentValue is initialized to the second value in the array.
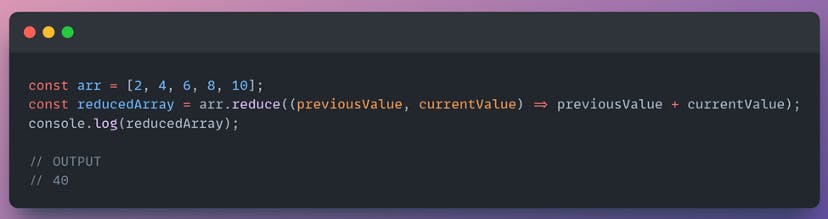
reduce() example
Find the sum of the numbers in the array.
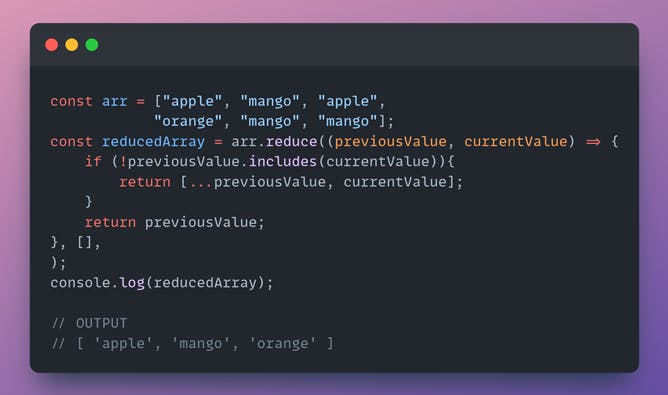
Remove the duplicates in the array.
Summary
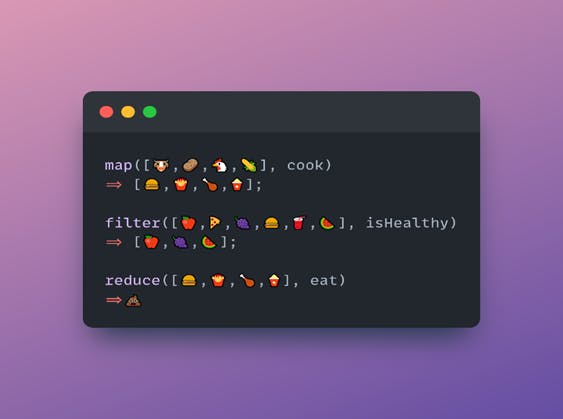
The illustration above summarizes this whole article. This is the best way to remember map, filter, and reduce.
GLOSSARY
Shallow copy
When there is an original object, a new object is created where the same values (as in the original objects) are copied. This is a shallow copy. The filter method creates a shallow copy of a portion of a given array, filtered down to just the elements from given array, filtered down to just the elements from the given array that pass the test implemented by the provided function.
Thank you for reading and engaging in my article. You can always save it and reference it later for clarification.
Further Reference
developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaSc..
